Business Intelligence Dashboard Definition Pdf
BI Dashboard Best Practices How to take advantage of state-of-the-art BI dashboards
Professional Business Intelligence Dashboards
Table of Content
1) What is a business intelligence dashboard?
2) What are the key benefits of a BI dashboard?
3) Top 10 BI dashboard best practices
4) Real world BI dashboard examples
5) Conclusion & Guidance
It's often said that knowledge is equal to power. While it isn't possible to apply this statement in a universal sense (and in fact, it's somewhat cliché), the notion does serve to highlight an important truth regarding today's digital world: consumer values are continually evolving. Data has never been more readily accessible. Approaches to communication are changing, and success in today's technology-driven world correlates directly to the quantity rather than the quality of one's information — metrics relating to the business, the client, the competitor, and the market. But IT departments no longer hold the exclusive access to data, and with BI dashboards, the knowledge is spread across the company, empowering every business user to create own, interactive reports, utilizing data visualization and spreading the knowledge with internal and external stakeholders.
Informed decision-making ultimately leads to greater access, opportunities, and technological advancement. Very often, the most important factor in determining success comes down to who engages in factual and informed decision-making and who follows hunches and suppositions. But what is one strategic business intelligence (BI) mechanism that is absolutely necessary in the digital age? A BI dashboard. How can you create one? Thanks to specific BI dashboard best practices.
Here, we'll talk about the importance of working with a business intelligence dashboard while outlining the 10 most essential best practices for success. These practices are developed by our experience as a BI provider working with hundreds of customers over the years and we've decided to share our extensive experience of conducting successful BI projects across the globe.
To put theory into practice, we will also present a hand-picked selection of real-world business intelligence dashboard examples based on different business goals or disciplines, created with a powerful BI dashboard creator that you can use for your own business needs. But first, let's give a bit of a background of the terms we use and the benefits they provide.
1) What Is A Business Intelligence Dashboard?
A BI dashboard — or business intelligence dashboard — is an information management tool that uses data visualization to display KPIs (key performance indicators) tracked by a business to assess various aspects of performance while generating actionable insights.
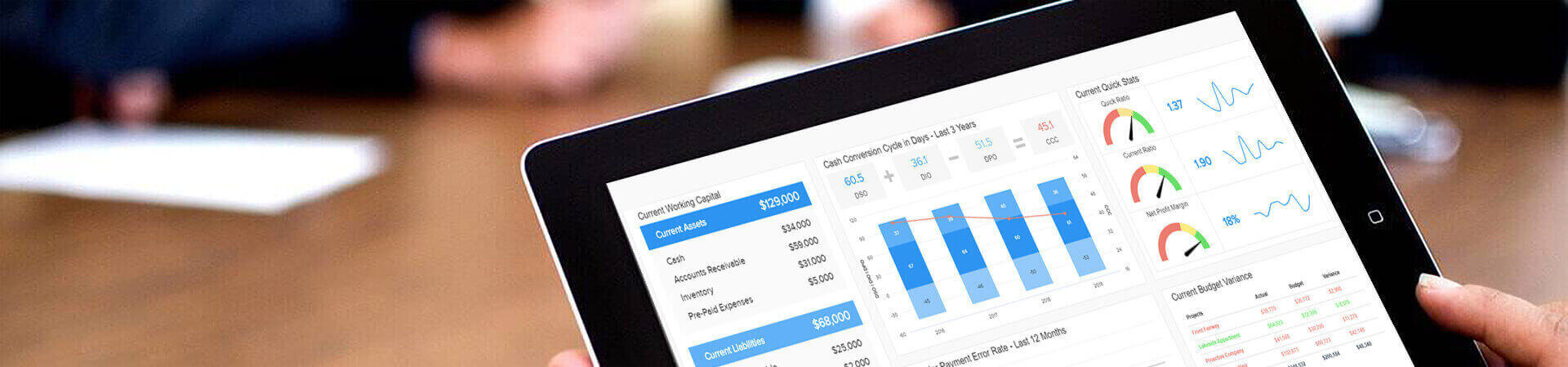
They are basically a tech-driven approach used to analyze and visualize information in an actionable way. Business intelligence dashboard design consolidates charts and graphs on a single screen, providing the reader with a big picture of the situation it is assessing. BI dashboard tools don't have a fixed, determined nature and adapt to the needs of the people building it, by displaying the metrics relevant to their function, industry or platform. Below you can find a professional BI dashboard example:

Such dashboards can have a lot of different features, mainly having a customizable interface, a certain level of interactivity as well as the possibility to pull data in real-time from multiple sources. By enabling the user to visualize otherwise complex and heavy raw data, they simplify the data processing for our brain and give readers an at-a-glance overview of the past, current, and future performance.
These kinds of cutting-edge solutions fuse the essential aspects of traditional business intelligence dashboards with their signature commitment to the user experience. Gone is pre-requisite SQL knowledge, absent are the myriad complex equations and language that makes sense to only the most experienced and qualified IT specialists. In its place comes a dashboard designed for use from the ground up – robust, accessible enough for an intern with no prior training, powerful enough for a CEO with years of frontline experience under their belt. From measuring budgetary efficiency, determining market trends, to understanding consumers – modern BI tools allow digital age businesses to easily identify the key performance indicators driving today's markets.
2) What Are The Key Benefits Of A BI Dashboard?
The purpose of a BI dashboard is to help business users make better-informed decisions by letting them gather, consolidate and analyze their data – and of course, visualize it in a meaningful way. They aim at simplifying a complex analysis of huge amounts of data, to avoid missing any trend or pattern. Often enough, they are overlooked or unspotted in an infinite table of numbers and figures, and the potential of such data remains untapped.
BI dashboards organize data cohesively while alleviating any potential clutter that can arise when working with complex sets of information while applying advanced intelligence tools to your various business strategies. Using highly visual data representations and tools, you can produce graphs, charts, and other powerful visualization instruments that empower you to interpret the data and transforming it into actionable insights that will benefit your business in many ways. To outline the unrivaled value of creating such a dashboard, here are the primary benefits of utilizing a BI dashboard:
Trend identification: Dynamic dashboards empower businesses across sectors to identify and analyze positive trends related to a wealth of business activities while isolating and correcting negative trends for improved organizational efficiency.
Increased efficiency: For the best results, decision-making should always be based on the right data — and a dashboard will allow you to achieve this. A business analytics dashboard improves efficiency by serving up relevant real-time data, allowing you to make informed, accurate decisions that will catalyze your success.
100% Accuracy: To take advantage of your competition, it is also important to have accurate data in planning, analysis, and reporting. This is achieved by real-time access to data, that can provide instant insights on how your business performs on an operational or strategic level. If all employees are informed at the right time and the at right moment, guesswork is completely eliminated, thus creating substance for making informed decisions.
Interactive data visualization: As more data sources emerge, there is a strong need to compile a centralized point of access where data can be presented in a clean way, with instant insight. Traditional spreadsheets such as Excel have become so crammed that making a business decision can end up in indefinite scrolling and searching for the right information. Since humans process visual data much faster than written, graphics are becoming the business standard for presenting information. And not just ordinary graphs and charts, but interactive, visualizing every information a business possesses, predicting outcomes and providing business users with instant, actionable insights.
Self-service features: It's possible to implement modern self-service BI easily and without the need for specific technical IT skills. As a result, a dashboard offers company-wide access to invaluable data-driven insights that people can share swiftly, providing a level of agility and mobility that traditional data processes simply cannot match.
Freedom & flexibility: Expanding on our previous points, the centralized and completely portable nature of a business intelligence dashboard means that it's possible to access and analyze invaluable business insights from a multitude of devices 24/7, wherever you may be in the world. This level of freedom and flexibility translates to increased productivity and enhanced business intelligence on a consistent basis — one of the key ingredients of success.
Advanced data analyst tools come in all shapes and sizes. From data mining and spreadsheets to local information systems, each available data solution plays a different role in maximizing value creation. To help you squeeze every drop of value from your BI efforts and ensure optimal BI dashboard design for specific strategies or goals, we'll explore the top 10 best practices that you can implement.
3) Top 10 BI Dashboard Best Practices To Follow
As mentioned, these best practices refer to methods and techniques made and recommended by our expertise from working on hundreds on BI projects with customers around the world to get the maximum value out of your dashboards and reports. These 10 key BI considerations hold all of the information you need to hit the ground running with your newfound data-powered organizational strategies, including practical advice on business intelligence dashboard design.

1. IDENTIFY YOUR REPORTING REQUIREMENTS
As you would do for any type of reporting – management, financial, marketing, etc. – the first thing you need to clarify is the "Ws": why do you need to report, and to whom? List all the stakeholders involved as well as the decision-maker and end-users. Once your target audience is defined, you will have a better idea of what will be on your dashboard.
Indeed, knowing who your readers will be will help you focus on specific aspects of the data that is relevant to them, to their needs, that matches their expectations and technical skills. To do so, you can schedule a phone or face-to-face interviews with different stakeholders to consolidate all of their reporting requirements.
When this is done, it will be much easier for you to choose from lists of KPIs, the ones that will fit your audience best. Remember that the purpose of a BI dashboard is to see clearly your business reality so that you can make the right decisions at the right time. The data analysis questions you'll ask will provide a framework and allow you to focus on specific aspects of your business performance – and that's when the KPIs come in. Pick the ones that translate the status of your business best and measure the evolution of your process towards your goals.
2. KNOW YOUR DASHBOARDS
Before selecting your tool, it is important to know what types of dashboards are available. Once you understand each type, you can make an informed decision regarding the purpose and implementation of your dashboard. Remember, informed decision-making for maximum ROI is the whole point!
Strategic: Strategic dashboards aggregate key organizational health indicators and help c-suite executives identify opportunities for organizational expansion. They detail the general health of an organization, not for the purposes of a complete analysis, but to provoke future thought and further independent analysis. The analyses are not overly complex and typically include more general data aggregations compared to other dashboard solutions.
Analytical: This type of dashboard is engineered to provide detailed data analyses pertaining to data trends (the what, the why, the how). Analytical dashboard solutions place a particular emphasis on measuring data variables in relation to time (week, month, year, etc.). An example would be to conduct an analysis of supply chain management, together with product sales, over a designated period of time in order to determine what trends, mutually dependent factors, and potential strategic consequences exist (if any). A great analogy for analytical dashboards would be that of a general medical practitioner. He or she may not be an expert in one specific medical field, but they can effectively monitor the overall health of the body by comparing current symptoms to what would be an ideal state of health. This is exactly the role of analytical dashboards. As analytical dashboards take into account a multitude of different measurables for the purposes of aligning goals with performance, they have a tendency to be complex and highly focused.
Operational: Where analytical dashboards monitor the overall health of an organization, operational dashboards focus on KPIs. They will vary depending on industry and audience (sales, marketing, finance, etc.), but they will always monitor the real-time operations of an organization or entity. Rather than analyze the general health of an organization (or "body"), operational dashboards will specialize in monitoring the functionality (and deviations) for various KPIs (or "organs") that exist within an entity. As an operational dashboard provides real-time information, they tend to contain less complex data.
Tactical: A reporting tool typically used for mid-level management, a tactical dashboard is incredibly analytical and drills down deep into several key areas of a company's internal processes. Tactical dashboards offer a great deal of insight into weekly trends and metrics and are pivotal in improving internal communication and formulating mid to long-term strategies across departments from marketing and finance right the way through to human resources.
3. DESIGN DATA TO AVOID CLUTTER
Once you have given thought of and selected the type of dashboard you desire to implement, you should begin focusing on concise and effective design. While an "easy on the eyes" design scheme may appear tempting, effective communication should always be your number one priority.
It is a major fallacy to assume that what you think is a more visually appealing dashboard will communicate more effectively with your data audience. Communication is a science, and BI dashboard design should reflect quick, concise and clear fact-based communications. One of the unfortunate tendencies of data professionals in the digital age is the self-defeating habit of overburdening audiences with clutter. This is why you should follow the 5-second rule, which states that your dashboard should provide the relevant information in about five seconds.
While its forms vary, the inherent nature of clutter will likely always remain the same… it will occupy cognitive space within the mind of the audience, and yet, simultaneously fail to have any substantive or beneficial impact. Not only will clutter fail to have a positive impact on an audience, but it will also create the appearance that data is more complex than its true nature. To avoid clutter, you must identify clutter. A great guide to identifying the characteristics and forms of clutter is the Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception. These six principles (discussed below) were defined by the Gestalt school of Psychology as the main principles outlining basic human interaction and order creation within the context of visual (i.e., data) stimulation. Let's briefly take a look at each principle.
Proximity: The principle of proximity dictates that we tend to group elements together based on their location or "proximity." This principle allows for the manipulation of perception through well placed and cleanly grouped data.
Similarity: The principle of similarity dictates that we are likely to group comparable elements together. This essentially means that from the visual perspective of the audience, similar colors, shapes, and fonts are expected to be grouped together. When applied to client communications, this principle can assist with the removal of unnecessary data elements.
Closure: The principle of closure refers to our propensity to "close the gap" and create complete elements. This concept applies even when portions of shapes and figures are missing.
Enclosure: The principle of enclosure dictates that if elements are controlled by a visual border or shading, we will tend to see the objects and elements as unique groups. Like prior principles, this principle can be employed as a foundation for graphical data presentation.
Continuity: The principle of continuity dictates that if separate linear elements are positioned within one another, we will tend to integrate all of the parts of the elements. Individual lines will then be viewed less as separate and more as a continuation of one central element.
Connection: The principle of connection dictates that our visual pairings are often strongest when there is an actual linear tie. That is, rather than associating elements via color, shape or spacing, we will use a direct lineal connection to establish the foundation for our visual relationship with data.
4. DESIGN DATA WITH A CLEAR VISUAL ORDER
One of the most influential factors impacting dashboard data analysis is the subconscious desire to achieve visual order. Disorder begets disorder, and if we fail to appreciate the value of a clean and clear data presentation, our data disorder will ultimately result in dashboard disorder. Let's take a look at the elements of a well-ordered dashboard, engineered for visual success.
Consistent Alignment: Ideal data alignment for dashboarding purposes is likely to be determined on a case by case basis. A good default rule is to have your most informative data positioned in the upper left (the upper left corner of the page is likely a leading candidate for informative text). Knowing what to place and where is as important as knowing what not to place. Therefore, a second general rule is to avoid ALL temptation to place diagonal elements and fill patterns. Diagonal data elements, especially those linear in nature, add little benefit while significantly reducing alignment efficiency.
White Space: Does white space equal wasted space? No! More is not always better. White space is a design term used to reference space within a presentation that is not allocated to any specific element. It is space void of all images, colors, texts, data, and other visible page elements. You should be keen to take advantage of the proven benefits of both "active" and "passive" white space (i.e., intentional and unintentional). Benefits include: enhanced design and balance, enhanced readability, appearance of sophistication as well as prioritized data elements.
Use of Contrast: Contrast should be viewed as closely related to white space. Both originate from the same family tree, but each one brings its own unique properties and features. You can, and should, experiment with both contrast and white space together. When combined, they have the potential to create an incredible one-two visual punch. More often than not, the contrast will be applied via a change in the data color scheme. This change, likely to be focused on a "point of emphasis" element, is intended to draw the viewer's attention to a specific and important data detail. Simple color and design variations will enhance the information gathering process and allow for an efficient, focused and comfortable data experience.
5. CHOOSE THE RIGHT DATA VISUALIZATIONS
We've covered vital elements of business intelligence best practices for dashboard design, and in many ways, visualization selection is an extension of these methods. The human brain digests visual information more efficiently than textual insights. This means that when you're working with your dashboard data, you should display it in a way that resonates with your audience on a deeper, more meaningful level. In doing so, you will ensure your data is transformed into actionable insights that ultimately drive the business forward.
BI dashboard imagery comes in many forms. To help you choose the right representation of your data, here's our guide to choosing the right types of data visualization for your reading pleasure. Below you find a short visual summary:
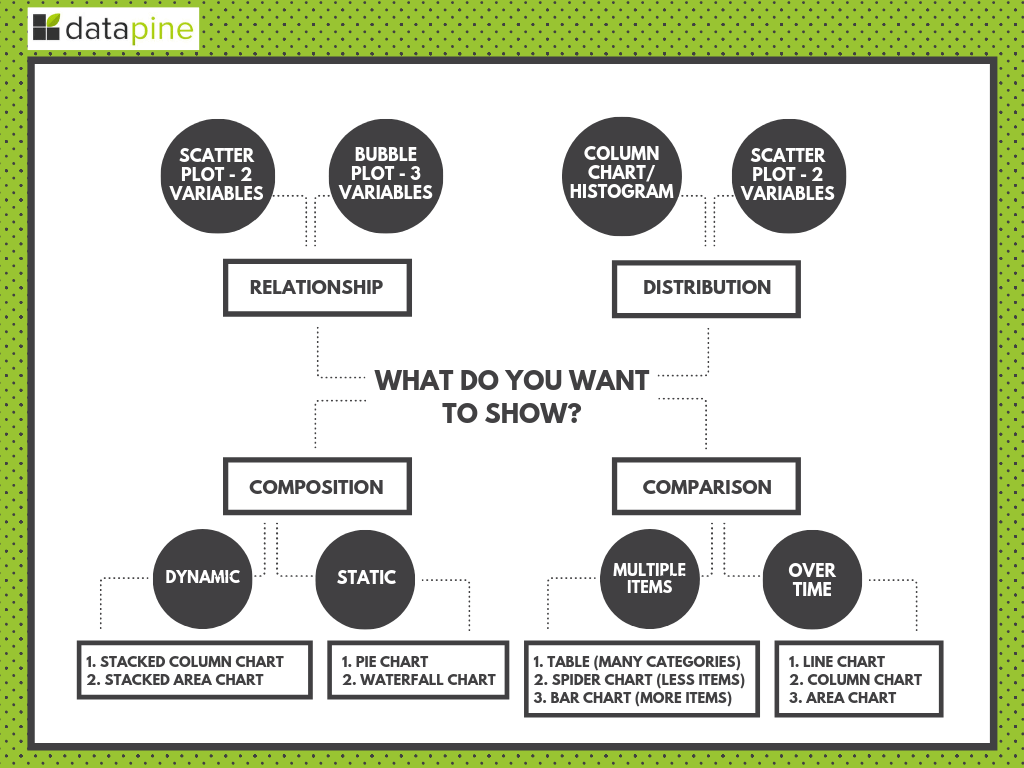
6. PROVIDE DATA CONTEXT
In order to properly analyze the role of data within a specific dashboard, everyone from the CEO to a first-year product salesperson needs to understand the notion of context. Data analyses and visual representations lacking data context will be limited in their utility and ROI. It is normal for data points to generate more questions than answers. However, data observers should be fully informed, nonetheless. For example, if a dashboard is monitoring product marketing effectiveness, and one of the data points included is total sales, this data point will be useless without knowing the measurement time frame. Is it this week? This month? This quarter? This fiscal year? Absent time-specific context, it is next to impossible to know the intended significance of the data. Also, answer yourself if you additionally need to develop KPI scorecards to update information on a periodical basis only.
A second but equally important part of the context is the currency. Selected data metrics must be up to date in order to reflect current trends and challenges. If not, there is almost no point in any analysis. Data arriving at the party out of date creates a margin of analysis error that is a slippery slope.
Data rooted in past circumstances is bound to create "fact-based" decisions that are no longer representative of current business environments. While the expectation isn't (and shouldn't be) minute-by-minute updates, data metrics should put your business in the best possible position to make informed decisions. For that to happen, data points should remain relatively current.
7. WEB-BASED ACCESS
This particular BI best practice is a matter of technological advancement, but also preference. In today's digital age, with the demand for real-time data updates, online business intelligence dashboards are the most invaluable tools a company can utilize. Web-based data sharing and analyses reach a wider audience and allow for greater collaboration with other data solutions. File-based publishing is an option if budgets and capabilities are limited, but this will negate one of the greatest advantages of remote synchronization.
When in doubt over which storage technique is right for your business, be sure to test each strategy and determine which system of implementation aligns more seamlessly with your organizational needs, capabilities, and goals. Remember! The ability to share real-time dashboards on web browsers, TV monitors and mobile devices will grant your business the data visibility it needs to stay in control of opportunities and trends. From data storage to real-time information delivery, to convenience… web-based dashboard solutions will seamlessly align with the need for mobility and flexibility in today's business landscape.
8. CONSIDER YOUR TARGET AUDIENCE
Considering your target audience is one of the most integral practices for BI dashboarding, and it's vital if you want to reap the best rewards for your BI-based efforts. When choosing data visualization types and crafting working designs for your dashboards, it's crucial to consider the end-user or the audience to which you're aiming your presentation.
Are your audience members internal stakeholders, potential investors, or existing company partners? Or are your internal dashboard users working on a specific campaign or part of a focused department? If so, what data access will they need? All of this information is integral to shaping your efforts to succeed. Sit down collaboratively and consider all of these questions before setting up your dashboard.
9. TELL A TALE WITH YOUR METRICS
Storytelling is a powerful best practice for any business, regardless of industry or sector — so use it to your advantage. A compelling narrative will not only capture the attention of your audience; it will also break down your information in an inspirational and digestible way. This approach will result in increased success across the board. To help enhance your KPI-driven storytelling efforts, here's our definitive guide to dashboard presentation and storytelling in the digital age.
10. REFINE - PERFECT - REPEAT
This is an often overlooked but integral element of business intelligence best practices — to ensure sustainable success, you must continue to improve and enhance your efforts. While your BI dashboards may be perfect for your strategies today, they might lose their relevance tomorrow. The digital world is in a constant state of flux, and to remain adaptable to change, it's vital to make continual improvements.
You should periodically work through steps 1 to 10, using your data as well as the landscape around you as a working guide. This is a practice that holds infinite value. Do this, and you'll set yourself apart from the pack time after time.
4) Real World BI Dashboard Examples & Templates
Best BI dashboards communicate key numbers in an understandable way while keeping the possibility to drill-down for more details. They prioritize the right metrics, personalize the content to the reader(s) and avoid clutter. Our BI dashboard examples we will present next are focused on various functions a company usually contains while applying all the best practices we have discussed. We're starting with the marketing department as one of the most vital functions within a company.
1. MARKETING KPI DASHBOARD
We have a strategic dashboard that collects key financial health indicators for the marketing department. It is a big-picture dashboard typically designed to c-suite executives that do not focus on specific marketing aspects (i.e. the numbers of clicks or impressions, the email open rate, etc.). Instead, the financial metrics displayed provide top managers and investors with the performance of the department over time and help them determine where their marketing dollars should go in the future.

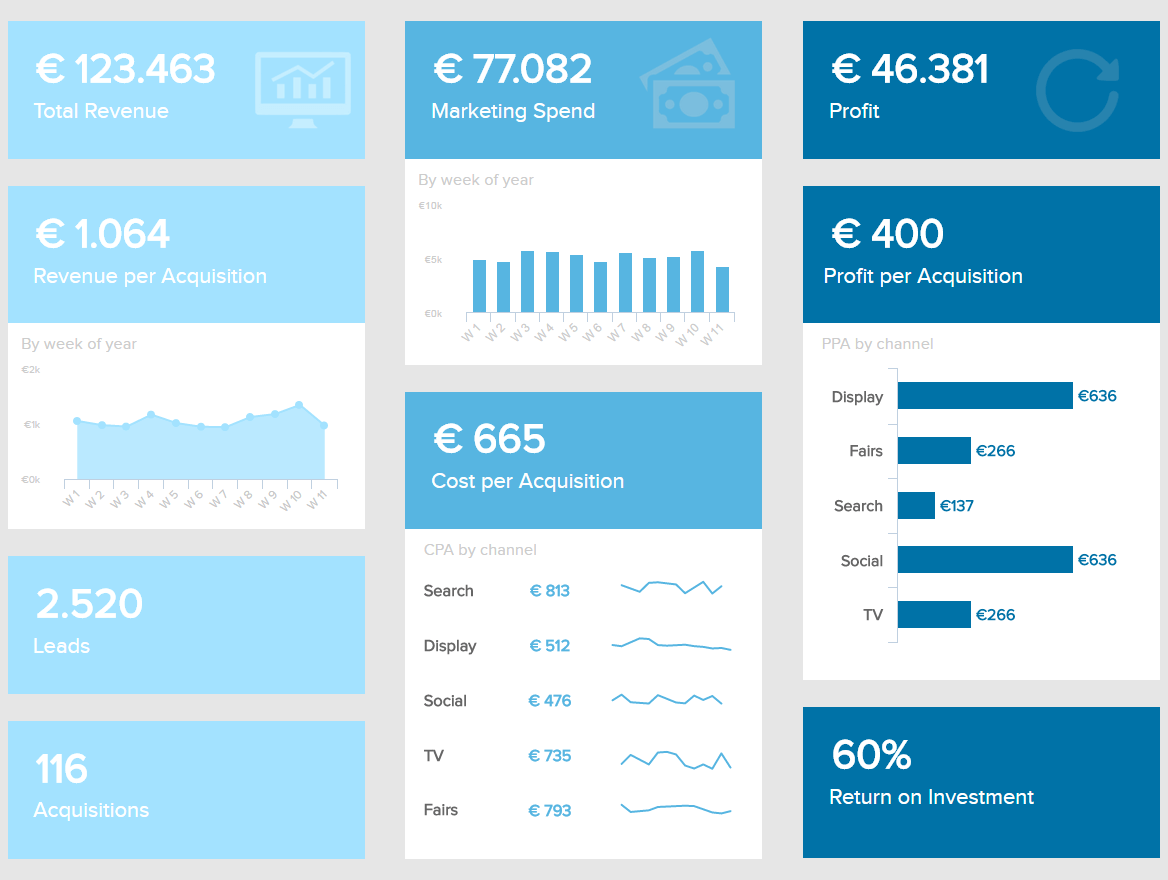
The design is consistent with several shades of blue that do not clash with each other, while the graphs and figures displayed are not cluttered and follow a clear visual order so every marketing KPI is comprehensible. The message of that dashboard is understood in a glance and the alignment and white space give a rest to the eyes, who are not struggling in getting to the point.
Next, let's move onto one of our best business intelligence dashboard examples relating to one of any business's most important activities — sales. Without this function, a company would not be able to move forward and increase profits. By utilizing online dashboard tools, the department can successfully monitor and outperform each sales target and goal.
2. SALES KPI DASHBOARD
One of the best business intelligence dashboards for profitability, our sales dashboard below is focused on helping you hit sales targets and foster growth on a consistent basis, boosting your KPI monitoring processes and, ultimately, bottom line. Concentrated on high-level metrics, this dashboard will enable you to cultivate a data-driven environment, crucial in generating more revenue and, ultimately, increasing profits.

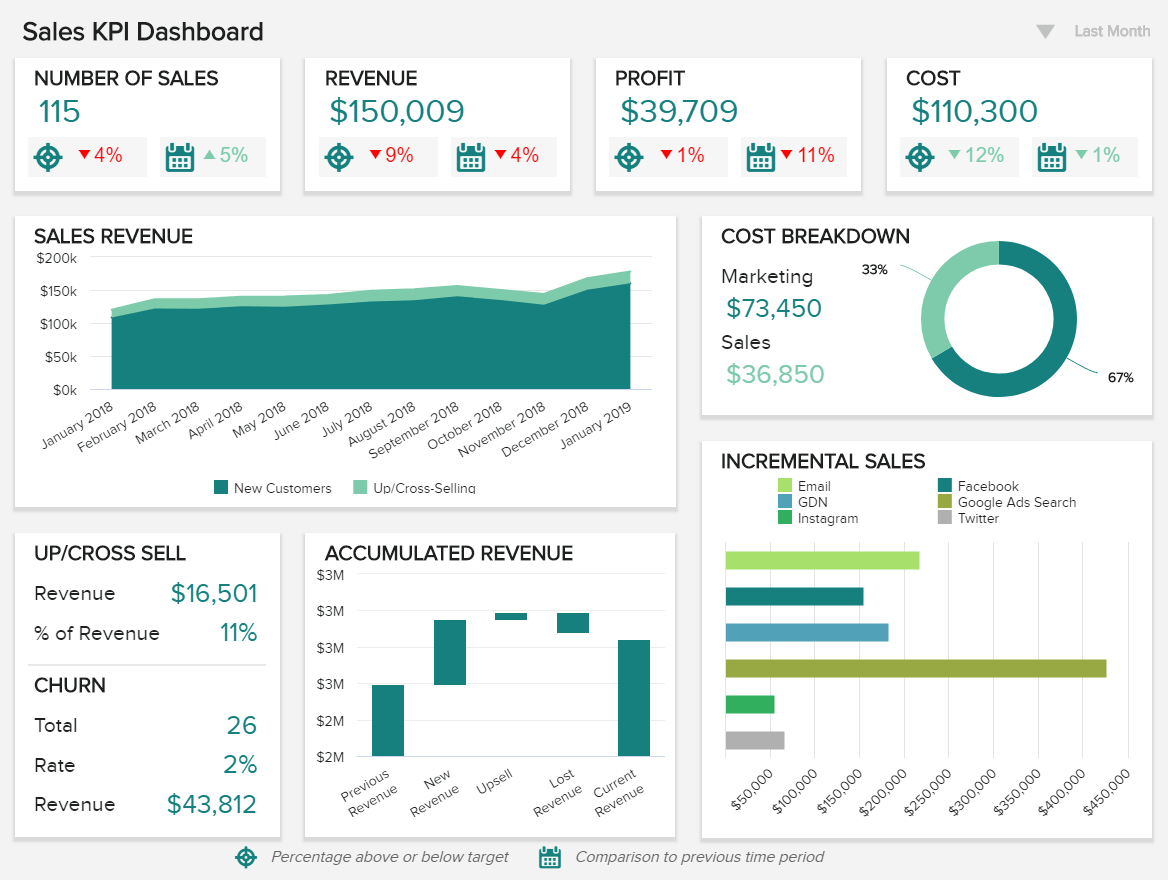
By offering clear, logical visualizations of your company's most critical sales data, it's possible to extract valuable insights at a glance while performing analysis that will help you strengthen inefficiencies while capitalizing on your strengths.
Working with dynamic sales KPIs including sales growth, sales target, acquisition cost, CLV (customer lifetime value), and ARPU (average revenue per unit), this dashboard offers all of the tools to make your business more economically efficient, and as a result, more valuable.
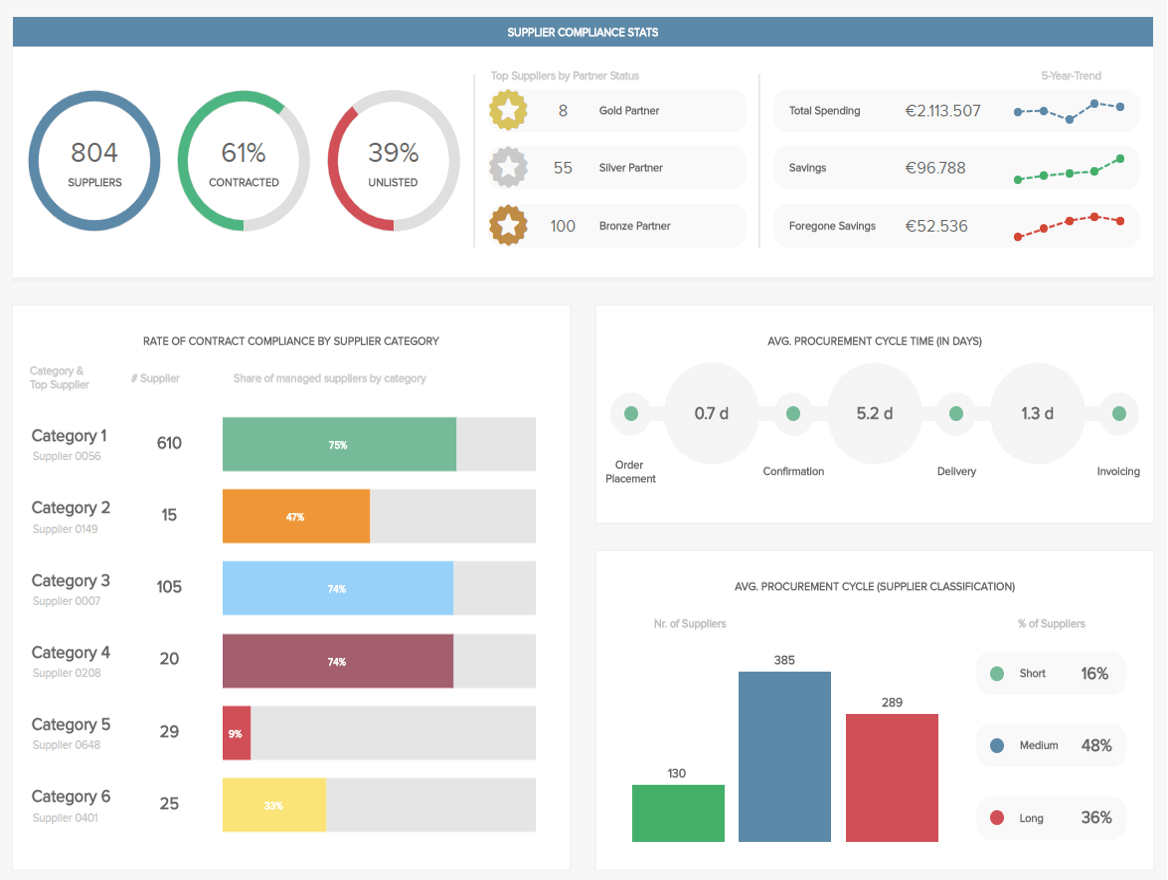
3. FINANCIAL KPI DASHBOARD
One of the best BI dashboard examples for those that need a general financial overview of a company or department, our financial KPI dashboard serves up a wealth of metrics based on improving processes and eliminating processing inefficiencies.

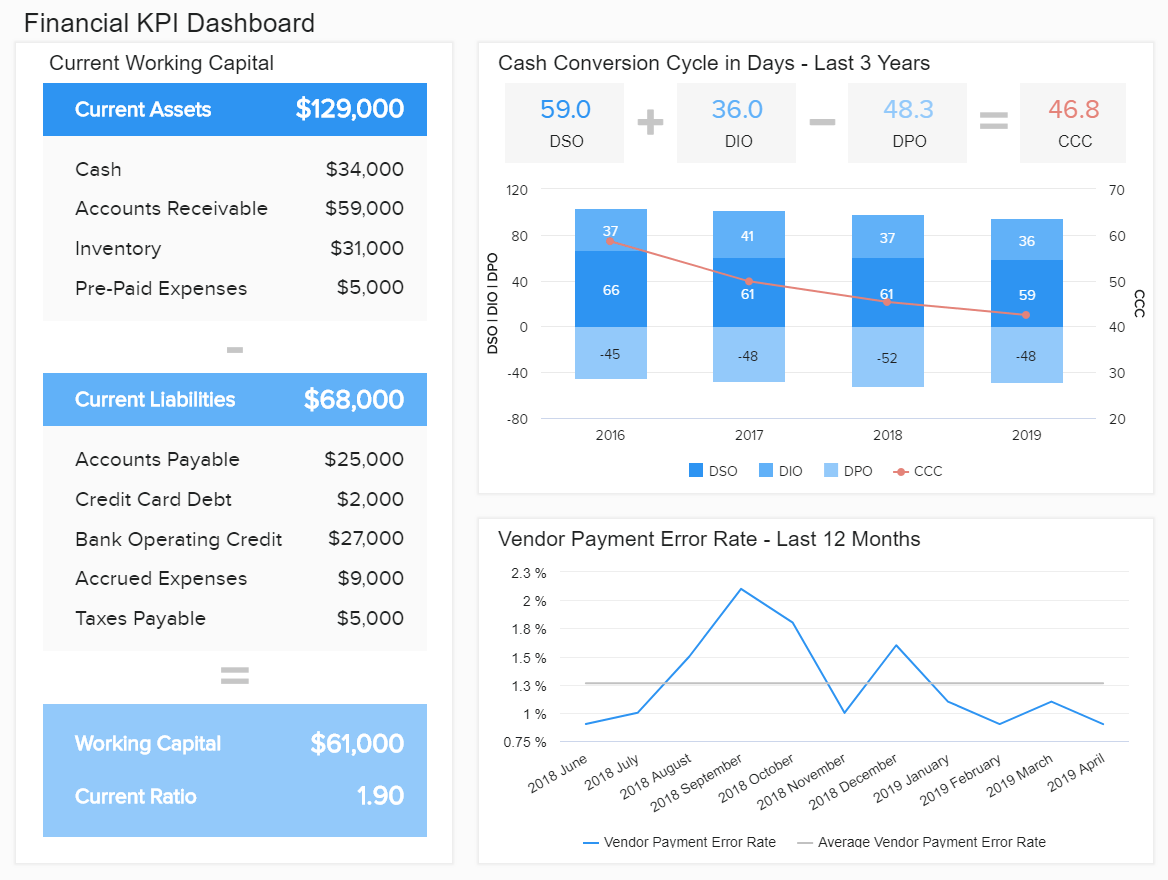
This financial dashboard sample breaks down a number of financial processes into digestible segments. You can gain a deep working insight into your working capital, cash conversion cycle, and vendor payment error rate. This mix of invaluable insights offers all of the key ingredients for developing seamless processes that help to save on unnecessary costs while significantly boosting productivity.
5) Conclusion & Guidance
Business intelligence and dashboards are extremely cost-effective by minimizing the potential for human error and streamlining the decision-making processes dependent on data interpretation. To help you on your way, you might want to consider datapine as your BI provider. Established in Germany with a long tradition of highest security layers in the world, datapine is continuously disrupting the EU and markets across the world, no matter if you need us for your management or data science efforts.
Freeing teams from IT bottlenecks, our BI solutions require no SQL knowledge and can be used by any business department. Built around an easy-to-use drag-and-drop interface, users can simply select the report elements they require and then leave the complex equations to our tool. Our software has been developed and refined with the help of companies from around the globe. Its function is based on real-life needs and wants, which means it understands the complex and myriad requirements of business function from the operational to the strategic, managerial to marketing, and offers support accordingly. It's this real-world application that gives rise to datapine's signature ease of use – from innovative data visualizations through to advanced data analysis tasks that were once complex are now as easy and pointing and clicking a mouse.
Finally, all common data sources can be integrated with a few clicks and with no software to download, any employee, in any location can begin to utilize dynamic real-time dashboards, automated reporting and data visualization instantly, including mobile, on-the-go solutions. With no prior training required, the barriers to wielding business analysis tools – requirements such as formal IT training and previous BI experience – disappear.
With personal access, a cloud-based structure that guarantees 24/7 access from any location and enterprise-level security layers, see what datapine's software can do for your business with a free 14-day trial!
Build professional business intelligence dashboards with a few clicks
Start your free trial and take advantage of modern BI dashboard software today!
Business Intelligence Dashboard Definition Pdf
Source: https://www.datapine.com/articles/bi-dashboard-best-practices
0 Response to "Business Intelligence Dashboard Definition Pdf"
Postar um comentário